A Federal Study Reveals Young Adults Are Three Times More Likely to Use Marijuana Almost Daily Compared to Alcohol
|
IN BRIEF
|
The landscape of substance use among young adults is witnessing a significant shift, as a recent federal study highlights a striking trend: individuals aged 19 to 30 are now nearly three times more likely to engage in daily or near-daily use of marijuana than alcohol. This transformation reflects evolving societal attitudes towards cannabis, particularly as legal implications and perceptions of harm continue to change in conjunction with public health discussions. As we delve further into the findings, the parameters of use within different age demographics paint a complex picture of substance consumption in contemporary American culture.
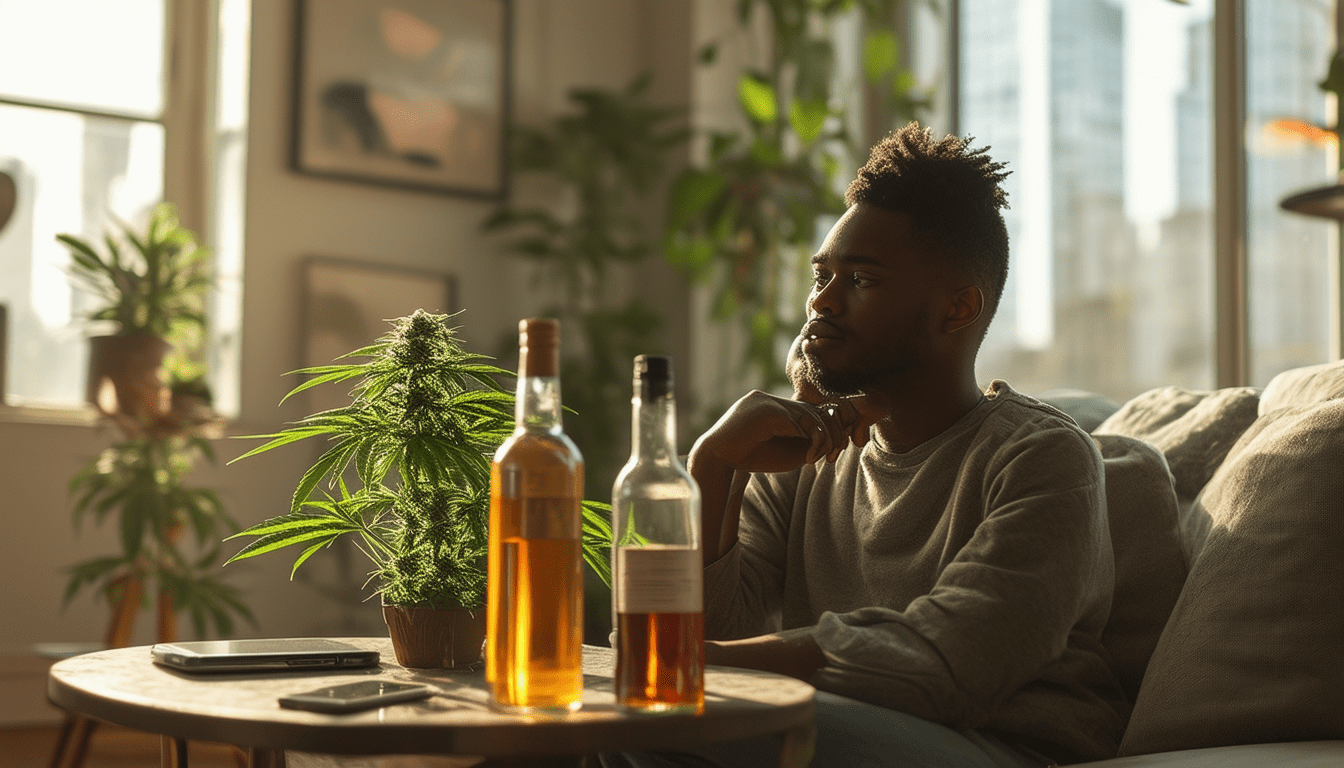

A recent government-backed study highlights a significant shift in substance use among young adults. The findings indicate that individuals aged 19 to 30 are nearly three times more likely to consume marijuana on a daily or near-daily basis than to drink alcohol. This analysis not only sheds light on changing patterns of substance use but also raises questions about the implications of these trends for public health and societal norms.
Understanding the Study
The research, led by Professor Megan E. Patrick from the University of Michigan, draws on the Monitoring the Future (MTF) Panel Study, which surveys approximately 20,000 people across three distinct age groups: 19 to 30, 35 to 50, and 55 to 65. The study, published in the journal Data Insight, reveals that in the youngest age group, a notable 10.4 percent reported daily or near-daily marijuana use, contrasting starkly with 3.6 percent who reported the same frequency of alcohol consumption.
Aging Patterns of Substance Use
The reports also unveil differing trends among older demographics. For individuals aged 55 to 65, frequent consumption of alcohol was more than twice as prevalent compared to marijuana use, with 11.4 percent acknowledging daily or near-daily drinking and 5.2 percent using cannabis at the same rate. In contrast, adults aged 35 to 50 exhibit nearly equal usage rates for both substances, with 7.8 percent for alcohol and 7.5 percent for marijuana. This variance highlights the generational perception of these substances, as younger adults seem to favor cannabis over alcohol.
Trends Across the Years
The study presents a striking increase in cannabis use over the past decade, emphasizing a significant rise among young adults and early midlife adults. Specifically, from 2013 to 2023, daily or near-daily use of marijuana increased by almost 75 percent, a notable change in consumption habits. Conversely, alcohol use has experienced a decrease among young adults, with a 35 percent drop over the past decade.
Social Implications of Changing Preferences
As these shifts occur, there is also a noticeable trend in societal perceptions toward marijuana and alcohol. The increasing prevalence of cannabis use among young adults juxtaposed with decreasing alcohol consumption raises important questions regarding public health messaging and legal frameworks governing these substances. Surveys indicate that many individuals now perceive cannabis as less harmful than alcohol, aligning with broader changes in legalization and societal acceptance.
Comparative Data from Other Studies
Other analyses have corroborated the trend indicating more U.S. adults use marijuana on a daily basis than alcohol. For instance, a recent survey indicated that an estimated 17.7 million Americans used marijuana daily or nearly daily in 2022 compared to 14.7 million who reported the same for alcohol. Moreover, studies suggest that individuals are increasingly substituting cannabis for alcohol, potentially owing to shifting perceptions of risk and evolving legalization efforts.
The Future of Substance Use Patterns
As state-level legalization movements progress and the societal stigma surrounding cannabis diminishes, the trajectory of substance use among young adults appears set to continue evolving. The implications of these shifts on the alcohol industry and public health are significant, with various analyses predicting that the alcohol market could face challenges as more consumers opt for cannabis over traditional alcoholic beverages.
Overall, the study emphasizes the need for an informed dialogue regarding substance use in contemporary society and highlights a potential crossover in daily consumption habits among younger demographics. If current trends persist, we may witness profound changes not only in substance use patterns but also in societal attitudes towards these substances in the near future.
Comparison of Daily Substance Use Among Age Groups
| Age Group | Usage Patterns |
| 19-30 | Marijuana: 10.4% DND; Alcohol: 3.6% DND |
| 35-50 | Alcohol: 7.8% DND; Marijuana: 7.5% DND |
| 55-65 | Alcohol: 11.4% DND; Marijuana: 5.2% DND |
| Overall Increase (2013-2023) | Cannabis: 75% increase; Alcohol: 35% decrease |
| Substitution Trends | Cannabis: Increasingly used instead of alcohol |
| Public Perception | Cannabis: Viewed as less harmful than alcohol |

A recent federal study has highlighted a significant shift in substance use trends among young adults. The findings demonstrate that younger individuals are now nearly three times more likely to indulge in marijuana consumption on a daily or near-daily basis compared to alcohol. This trend sheds light on changing social habits and perspectives regarding these substances, particularly among the ages of 19 to 30.
Understanding the Data: Frequency of Use
The analysis led by researchers from the University of Michigan utilized data from the Monitoring the Future Panel Study. The study surveyed approximately 20,000 participants across three distinct age groups, focusing on their patterns of daily or near-daily use of marijuana and alcohol. Among the youngest demographic, 10.4 percent reported using marijuana daily compared to only 3.6 percent for alcohol, illustrating a noticeable preference for cannabis.
Shifts in Substance Preferences Across Ages
As the study delineates, older age groups exhibit differing trends. In the group aged 55 to 65, alcohol remains the more commonly used substance, with an overwhelming 11.4 percent reporting frequent drinking compared to just 5.2 percent who indicated daily marijuana use. Interestingly, those categorized as “early midlife adults”—ages 35 to 50—demonstrated similar rates of daily consumption for both substances, leading to a complex landscape of usage patterns across age cohorts.
The Rise of Cannabis Use Over Time
Over the last decade, patterns of consumption have experienced a notable transformation. The study indicates that daily cannabis use among young adults has surged by nearly 75% over a span of ten years, marking a significant cultural shift in acceptance and preference for marijuana as an alternative to alcohol. In stark contrast, alcohol consumption among young adults has declined, raising questions about the reasons behind this substitution trend.
Implications for Alcohol Industry and Public Health
The implications of these findings are far-reaching. With a growing number of young adults opting for marijuana, the alcohol industry faces potential challenges. Shifts in substance use can influence public health initiatives, driving discussions about the risks and benefits associated with both substances. As society’s perception of cannabis evolves, it remains critical to monitor how these trends impact overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Future
This pivotal study serves as a crucial indicator of changing societal norms, particularly regarding substance use among younger generations. As more states move towards legalization and the acceptance of marijuana grows, future research is essential to understand the long-term ramifications of these trends on public health and the alcohol market.
- Demographics: Focuses on young adults aged 19 to 30.
- Frequency of Use: Daily or near-daily cannabis use exceeds alcohol consumption.
- Statistics: 10.4% of young adults use marijuana daily, while only 3.6% use alcohol.
- Historical Trend: Cannabis use has increased by nearly 75% over the past decade.
- Generational Differences: Older adults (55-65) more likely to drink alcohol than use cannabis.
- Substance Substitution: Younger demographics replacing alcohol with cannabis.
Overview of the Study
A recent federal study indicates that young adults between the ages of 19 and 30 are nearly three times more likely to consume marijuana on a daily or near-daily basis than alcohol. Conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, this analysis draws on data from the Monitoring the Future Panel Study, which surveyed approximately 20,000 individuals across various age groups. The findings indicate a significant shift in substance use patterns, with young adults showing a strong preference for cannabis compared to their alcohol consumption.
Understanding the Shift in Substance Use
The increase in marijuana use among younger adults highlights a broader cultural trend that may stem from shifting societal attitudes towards cannabis. The perception of marijuana has evolved, with many young people viewing it as a less harmful alternative to alcohol. This reassessment of risk may account for the significant 75% increase in daily or near-daily cannabis consumption among this demographic over the last decade.
Factors Influencing Substance Use
Several factors contribute to the rise in marijuana use among young adults. First, the increasing legalization of cannabis in various states has made it more accessible. As the stigma surrounding marijuana diminishes, more individuals may feel comfortable using it openly. Furthermore, educational campaigns emphasizing its medicinal and therapeutic benefits may also play a role in this growing acceptance.
Comparative Analysis of Marijuana and Alcohol Consumption
The data reveals a stark contrast in how these substances are consumed across age groups. Among young adults, 10.4% report using marijuana daily or nearly every day, in contrast to just 3.6% who report similar alcohol use. In other age demographics, trends appear to shift, with those aged 55 to 65 reporting a notably higher prevalence of alcohol consumption over marijuana.
Implications for Public Health
This shift in usage patterns presents significant public health implications. With the decline in alcohol consumption among young adults, there may be potential benefits such as reduced instances of alcohol-related harm, which has been linked to various health risks. However, the increase in cannabis use also raises concerns regarding potential negative health outcomes, including mental health issues and impairment.
Education and Prevention Strategies
To address these changing trends, it is essential to implement effective education and prevention strategies. Public health campaigns should focus on providing accurate information about both marijuana and alcohol, emphasizing the importance of responsible use. These campaigns can help to mitigate any potential risks associated with increased cannabis consumption while reminding young adults of the dangers of alcohol abuse.
Monitoring Future Trends
Continued research and surveillance of substance use trends are critical for understanding the long-term implications of this shift. By monitoring usage patterns among different demographics, public health officials can adapt their strategies to promote healthier behaviors effectively. It is vital to view these trends holistically, considering factors such as legality, social norms, and cultural perceptions.
As the federal study highlights, the landscape of substance use among young adults is evolving, and it is crucial to understand the underlying reasons for this change. By fostering open dialogues, conducting more in-depth research, and implementing effective educational strategies, society can better navigate the implications of this transition and promote the well-being of future generations.
FAQ: Young Adults and Daily Substance Use Trends
What did the federal study reveal about young adults’ substance use? The study found that young adults are nearly three times more likely to use marijuana on a daily or near-daily basis compared to alcohol.
What age group was included in the study? The study surveyed individuals across three distinct age groups: ages 19 to 30, 35 to 50, and 55 to 65.
What is the specific percentage of young adults using marijuana daily? Among 19 to 30-year-olds, 10.4 percent reported daily or near-daily use of marijuana.
How does this compare to alcohol use among the same age group? Only 3.6 percent of the same age group reported daily or near-daily alcohol use.
What trends were observed in older age groups? Among individuals aged 55 to 65, frequent alcohol consumption was more than twice as prevalent as cannabis use, with 11.4 percent reporting daily drinking compared to 5.2 percent using cannabis daily.
What changes in substance use patterns have been observed over the past decade? The study indicated an increase of nearly 75 percent in daily or near-daily cannabis use among young adults from 2013 to 2023, while alcohol use has decreased in the same demographic.
What was the trend for early midlife adults aged 35 to 50? This group showed almost equal rates of alcohol and cannabis use, with 7.8 percent reporting daily alcohol use compared to 7.5 percent for cannabis use.
How has alcohol consumption changed among young adults over the years? The study found that daily drinking among young adults has decreased approximately 35 percent over the past decade.
Is there a general perception shift regarding alcohol and cannabis? Yes, recent surveys indicate that many Americans view cannabis as less harmful than alcohol and tobacco, reflecting a broader cultural shift in attitudes towards these substances.




Post Comment